IoT Self-Driving Car
This lab was done as part of the CS437 Internet of Things curriculum
In this lab, I engaged in the construction of a self-driving IoT device, utilizing a Raspberry Pi 4B, a Raspberry Camera for visual perception, and a SunFounder Car Kit serving as the chassis. This project serves as a fundamental exercise to comprehend the operational principles resembling those of real-life Tesla or self-driving cars. The programming aspect of this task is implemented using Python.
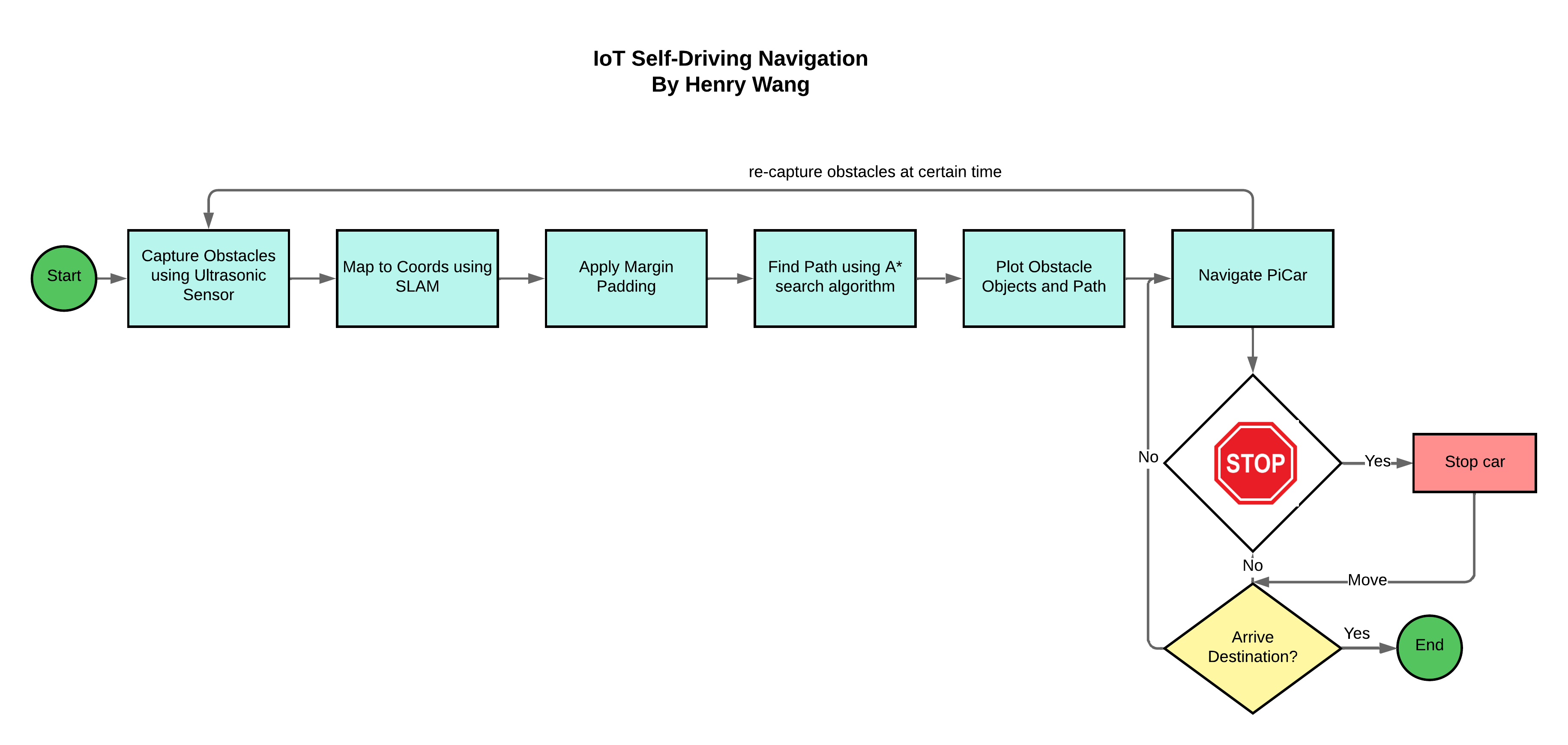
For processing the data from the ultrasonic sensor, a numpy array map data structure is employed. The data is stored in a numpy array using binary representation (0s and 1s), and the SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) algorithm is used for the mapping. To achieve object detection through computer vision, the project makes use of the OpenCV library, which leverages neural networks for automated object recognition. OpenCV is primarily employed for image processing, while the TensorFlow Lite interpreter API is utilized specifically for object detection purposes. Utilizing the map that was created, a graph search algorithm, in this case, the A* algorithm, is employed to find the shortest path between two points. A* is chosen as it prioritizes specific paths, resulting in reduced memory usage and potentially faster execution. To code this part, I utilize this python library, PyAstar2D, to calculate the A* path. As the car moves along its trajectory, it continuously rescans and recalculates its path based on the updated data from the environment.
Skills:
Raspberry Pi Python Sensors (Ultrasonic) Algorithms (A*, SLAM) Object Recognition (OpenCV, TensorFlow Lite) AWS IoT Core AWS IoT Greengrass AWS EC2 AWS Lambda